Elevate your gardening game with 2 tiered garden ideas that maximize space, add visual interest, and boost productivity. Dive into a world of innovative designs and practical tips to transform your outdoor space into a flourishing oasis.
Design Concepts
Two-tiered gardens offer unique advantages and challenges compared to traditional single-level designs. They can maximize space utilization, create visual interest, and improve drainage. However, they also require careful planning and maintenance to ensure plant health and aesthetic appeal.
Advantages
- Increased Space Utilization:Tiered gardens allow for vertical gardening, increasing the growing area without expanding the footprint.
- Enhanced Aesthetics:The elevation and varying heights create a dynamic visual effect, adding depth and interest to the garden.
- Improved Drainage:The elevated tiers facilitate water drainage, reducing the risk of root rot and promoting healthy plant growth.
Disadvantages
- Construction Complexity:Building two-tiered gardens requires more materials and labor compared to single-level designs.
- Maintenance Challenges:Watering, fertilizing, and weeding can be more difficult in elevated tiers, especially during extreme weather conditions.
- Limited Plant Selection:The elevation and potential wind exposure can restrict the choice of plants that can thrive in two-tiered gardens.
Layout Options
Two-tiered gardens come in various shapes and sizes, catering to different space constraints and aesthetic preferences:
- Rectangular:The most common layout, offering a classic and organized look.
- Circular:Creates a softer, more organic feel, ideal for smaller spaces.
- Asymmetrical:Allows for creative expression and can complement irregular-shaped gardens.
Elevation Impact
The elevation of the tiers significantly influences plant selection and maintenance:
Plant Selection:Plants suited for higher elevations include drought-tolerant species, wind-resistant varieties, and those with shallow root systems. Lower tiers can accommodate moisture-loving plants and deeper-rooted varieties.
Maintenance:Elevated tiers require more frequent watering, especially during dry spells. Mulching and using drip irrigation can help conserve moisture and minimize evaporation.
Plant Selection
When selecting plants for your two-tiered garden, it’s crucial to consider factors such as sunlight exposure, drainage, and space availability. The upper tier, which receives more sunlight, is ideal for sun-loving plants that require well-drained soil, while the lower tier, with less sunlight, is suitable for shade-tolerant plants that prefer moist soil.
Suitable Plants for Two-Tiered Gardens
The following table provides a comparison of suitable plants for the upper and lower tiers of a two-tiered garden:
| Upper Tier | Lower Tier |
|---|---|
| Sunflowers | Hostas |
| Marigolds | Ferns |
| Petunias | Impatiens |
| Zinnias | Begonias |
| Salvia | Astilbe |
Plant Combinations for Visual Interest
To create visual interest in your two-tiered garden, consider planting a variety of plants with contrasting colors, textures, and heights. For example, you could plant a tall sunflower on the upper tier with a trailing petunia cascading down the lower tier.
Another visually appealing combination is planting a bed of colorful zinnias on the upper tier and a border of ferns on the lower tier.
Materials and Construction
Two-tiered gardens require sturdy materials that can withstand the weight of soil and plants. Popular choices include wood, stone, and raised bed kits.Wood is a versatile material that is easy to work with and can be stained or painted to match your decor.
Stone is a more durable option, but it is also more expensive and difficult to install. Raised bed kits are a good option for those who want a quick and easy way to create a two-tiered garden.
Construction Steps
The first step in constructing a two-tiered garden is to level the ground. This will ensure that the garden is stable and that water does not pool in the lower tier. Once the ground is leveled, you can begin assembling the frame for the garden.If
you are using wood, you will need to cut the pieces to size and assemble them using screws or nails. If you are using stone, you will need to stack the stones in a pyramid shape and secure them with mortar.
Raised bed kits come with all of the necessary pieces and instructions for assembly.Once the frame is assembled, you can fill it with soil and plants. Be sure to use a good quality potting mix that is well-drained. You can also add a layer of mulch to the top of the soil to help retain moisture and suppress weeds.
Diagram of Construction Process
[Image of a two-tiered garden with a diagram of the construction process]
Soil and Drainage
Proper soil preparation is crucial for the success of two-tiered gardens. The soil should be well-draining to prevent waterlogging, which can lead to root rot and other problems. Raised beds are a great option for two-tiered gardens, as they provide good drainage and can be filled with a custom soil mix that is ideal for the plants you are growing.When
preparing the soil for your two-tiered garden, start by removing any weeds or debris. Then, till the soil to a depth of at least 12 inches. If the soil is compacted, you may need to till it twice. Once the soil is tilled, add organic matter such as compost or manure.
This will help to improve the soil’s drainage and fertility.
Irrigation and Fertilization

Maintaining proper hydration and nutrient levels is crucial for the success of two-tiered gardens. Different plants have varying water and fertilizer requirements, so understanding their specific needs is essential.
Irrigation Methods
Drip irrigation is a highly efficient method for two-tiered gardens. It delivers water directly to the roots, minimizing evaporation and water waste. Soaker hoses, placed along the base of plants, provide a slow and steady supply of moisture.
Hand watering can be effective, but requires more time and attention. Use a watering can with a narrow spout to direct water accurately. Avoid overwatering, as it can lead to root rot.
Fertilization Schedule
Fertilize plants regularly to provide essential nutrients. Use a balanced fertilizer diluted to half strength and apply it according to the manufacturer’s instructions.
- Spring: Apply a nitrogen-rich fertilizer to encourage leafy growth.
- Summer: Use a balanced fertilizer to support flowering and fruiting.
- Fall: Apply a phosphorus-rich fertilizer to promote root development.
- Winter: Most plants are dormant and do not require fertilization.
Organic Fertilizers and Compost
Organic fertilizers, such as compost and manure, are beneficial for two-tiered gardens. They improve soil structure, increase water retention, and provide a slow-release source of nutrients.
Compost can be made from kitchen scraps, yard waste, and other organic materials. It is a valuable source of nutrients and organic matter.
Maintenance and Troubleshooting
Maintaining a two-tiered garden requires regular attention to ensure the health and productivity of your plants. Here’s a guide to help you keep your garden thriving:
Watering
Water your plants deeply and regularly, especially during hot and dry weather. The upper tier dries out faster than the lower tier, so check the moisture levels frequently and water accordingly.
Weeding
Weeds compete with your plants for water, nutrients, and sunlight. Regularly remove weeds by hand-pulling or using a hoe. Mulching around your plants can help suppress weed growth.
Pest Control
Monitor your plants for pests such as aphids, spider mites, and whiteflies. Treat infestations promptly using organic or chemical methods. Companion planting and beneficial insects can help deter pests.
Common Problems
- Poor drainage:Ensure your raised beds have adequate drainage holes to prevent waterlogging, which can lead to root rot.
- Nutrient deficiency:Fertilize your plants regularly to replenish essential nutrients. Organic matter like compost can also improve soil fertility.
- Overcrowding:Avoid planting too many plants in your raised beds. Overcrowding can restrict growth and increase the risk of disease.
Extending the Growing Season
To extend the growing season in two-tiered gardens, consider using row covers or cold frames to protect plants from frost. You can also plant cold-tolerant varieties and use raised beds to create a warmer microclimate.
Creative Designs: 2 Tiered Garden Ideas
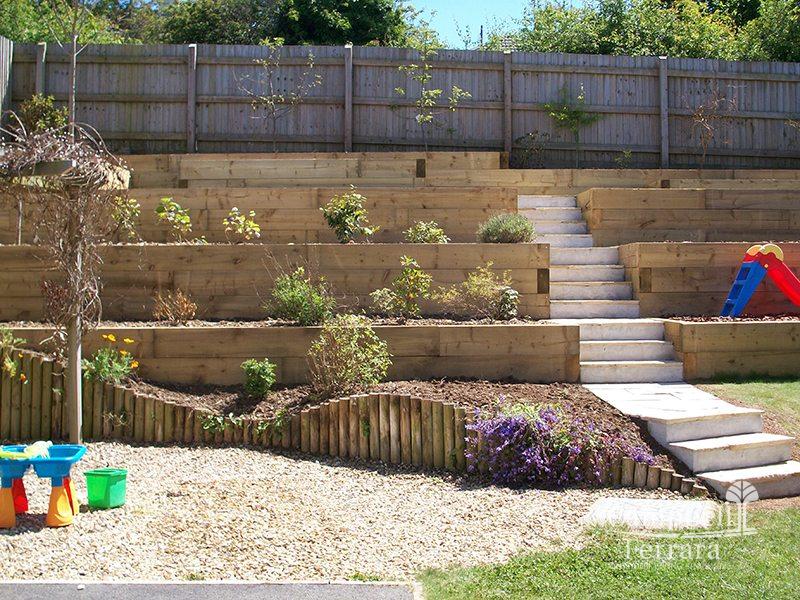

Two-tiered gardens offer ample scope for creative designs, allowing you to maximize space and create visually stunning outdoor areas.
Vertical gardens and espaliered plants can transform two-tiered structures into living walls, adding a touch of greenery and enhancing privacy. By training plants to grow vertically, you can create stunning displays that draw the eye upwards and make the most of limited space.
Trellises, Arches, and Decorative Elements
Trellises, arches, and other decorative elements can elevate the aesthetic appeal of two-tiered gardens, providing support for climbing plants and creating charming focal points.
- Trellises:Trellises provide a vertical framework for plants to climb, creating a lush and textured backdrop. Choose trellises with intricate designs or natural materials like wood or bamboo to add character to your garden.
- Arches:Arches create elegant and welcoming entrances to two-tiered gardens, framing the space and inviting visitors to explore. Plant climbing roses, clematis, or wisteria on arches to create a romantic and fragrant atmosphere.
- Decorative Elements:Incorporate decorative elements such as statues, fountains, or wind chimes into your two-tiered garden design. These elements add visual interest and create a sense of tranquility and charm.
Companion Planting
Companion planting is the practice of planting different species of plants together to create mutually beneficial relationships. In two-tiered gardens, companion planting can improve plant growth, enhance pest resistance, and increase overall productivity.
One of the key principles of companion planting is to group plants with complementary needs. For example, nitrogen-fixing plants, such as beans and peas, can be planted alongside heavy feeders, such as tomatoes and corn, to provide them with a steady supply of nitrogen.
Additionally, plants with different root depths can be planted together to utilize different levels of soil nutrients.
Examples of Companion Planting Combinations
- Tomatoes and basil:Basil repels insects that can damage tomatoes, while tomatoes provide shade for basil.
- Carrots and onions:Onions deter carrot flies, while carrots loosen the soil for onions.
- Beans and corn:Beans fix nitrogen in the soil, which benefits corn, while corn provides support for the beans to climb.
Importance of Crop Rotation
Crop rotation is another important aspect of companion planting in two-tiered gardens. By rotating crops each season, you can prevent soil-borne diseases, improve soil fertility, and reduce the buildup of pests and weeds.
Sustainability
Two-tiered gardens are inherently sustainable due to their efficient use of space and resources. By maximizing vertical space, they reduce the need for sprawling gardens, conserving valuable land. They also promote water conservation by capturing rainwater and utilizing it effectively.
Furthermore, the vertical structure allows for improved air circulation, reducing disease and pest problems, thus minimizing the need for chemical treatments.
Recycled Materials and Organic Practices, 2 tiered garden ideas
Creating sustainable two-tiered gardens involves using recycled materials such as old tires, pallets, or plastic bottles as containers. These materials not only reduce waste but also provide unique and creative gardening solutions. Additionally, employing organic practices like composting and using natural pest control methods further enhances the sustainability of these gardens.
Inspiration and Case Studies
Discover a world of two-tiered garden brilliance. Explore inspiring examples, learn from case studies, and gather wisdom from those who have cultivated thriving vertical wonders.
Our journey takes us to diverse climates and conditions, showcasing gardens that have defied space limitations and flourished in harmony with their surroundings.
Exemplary Two-Tiered Gardens
- The Hanging Gardens of Babylon:A legendary two-tiered marvel, said to have been adorned with lush greenery and cascading waterfalls.
- The Gardens of Versailles:A grand display of tiered parterres, showcasing intricate geometric designs and colorful blooms.
- The Butchart Gardens in Canada:A sunken two-tiered garden featuring a vibrant tapestry of flowers, trees, and water features.
Case Studies of Success
Delve into the stories of gardeners who have transformed their spaces with two-tiered gardens:
- Sarah’s Urban Oasis:A small city balcony transformed into a thriving two-tiered sanctuary with herbs, vegetables, and colorful annuals.
- John’s Hillside Haven:A sloping backyard terraced into a two-tiered paradise, featuring fruit trees, a vegetable patch, and a cozy seating area.
- Maria’s Coastal Retreat:A seaside garden with two-tiered raised beds, designed to withstand strong winds and salt spray, showcasing succulents, coastal plants, and herbs.
Lessons Learned
Through the experiences of these gardeners, we glean valuable insights:
- Planning is Key:Careful planning ensures efficient use of space, proper drainage, and optimal plant selection.
- Vertical Gardening Techniques:Employ techniques like trellising, hanging baskets, and stacked planters to maximize vertical space.
- Water Management:Two-tiered gardens require attention to water flow and drainage, utilizing drip irrigation or raised beds for optimal moisture control.
Ultimate Conclusion
From lush plant combinations to clever construction techniques, 2 tiered garden ideas offer endless possibilities for creating a thriving and visually stunning outdoor haven. Embrace the joy of gardening with these inspiring concepts and practical solutions.
FAQ Resource
What are the benefits of 2 tiered gardens?
Enhanced space utilization, improved drainage, increased plant diversity, and ergonomic gardening.
What materials can be used to build 2 tiered gardens?
Wood, stone, bricks, concrete blocks, and raised bed kits.
How do I choose plants for my 2 tiered garden?
Consider sunlight exposure, drainage requirements, and companion planting principles.
What are some creative design ideas for 2 tiered gardens?
Vertical gardens, espaliered plants, trellises, arches, and decorative elements.